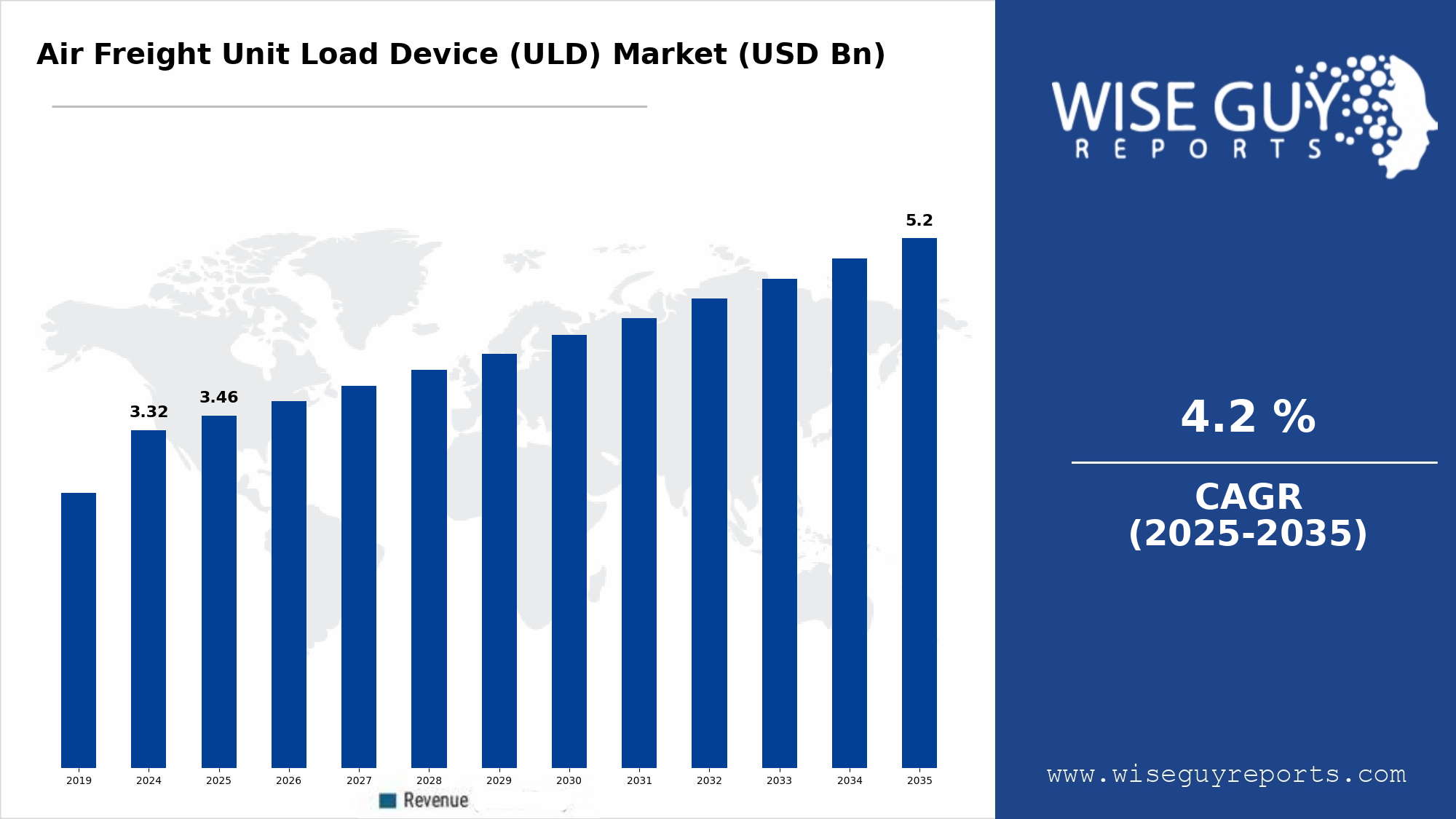
Air cargo has become the backbone of the global e-commerce supply chain. Customers expect fast delivery, cross-border shipments, and accurate parcel handling — and these logistics demands rely heavily on Unit Load Devices (ULDs) for efficiency, security, and organization during air transport.
E-Commerce Logistics Reshaping ULD Requirements
The rapid growth of online retail is increasing air freight volumes at an unprecedented pace. The Air Freight Unit Load Device (ULD) market is benefiting directly from this expansion, with rising demand for safe parcel stacking, temperature-controlled delivery, return logistics efficiency, and express freight management. Cargo reliability and fast aircraft turnaround time are essential for e-commerce fulfilment networks.
Smaller, Frequent Shipments Require Organized Cargo Solutions
Unlike traditional freight, e-commerce orders often consist of high parcel counts with varying dimensions and special-care requirements. ULDs provide structured stacking and load security that reduce in-flight damage and enable faster ground handling — critical for meeting next-day and express delivery expectations.
Cold-Chain and High-Value Fulfilment Growth
Online demand for perishables, food delivery kits, and pharmaceutical products is accelerating cold-chain shipping requirements. ULDs designed for temperature control help prevent quality loss and regulatory non-compliance, expanding adoption across perishable cargo segments.
Expanding Air Cargo Networks Supporting ULD Production
New air cargo routes, dedicated freighter fleets, and expansion of regional fulfilment hubs are increasing ULD circulation worldwide. The need for scalable, reusable, and efficient air containers continues to rise across e-commerce-driven freight corridors.
Conclusion
As global e-commerce continues to surge, ULDs will remain essential for timely and secure air freight movement. Their role in cargo organization, safety, and temperature management ensures strong long-term adoption across the digital retail ecosystem