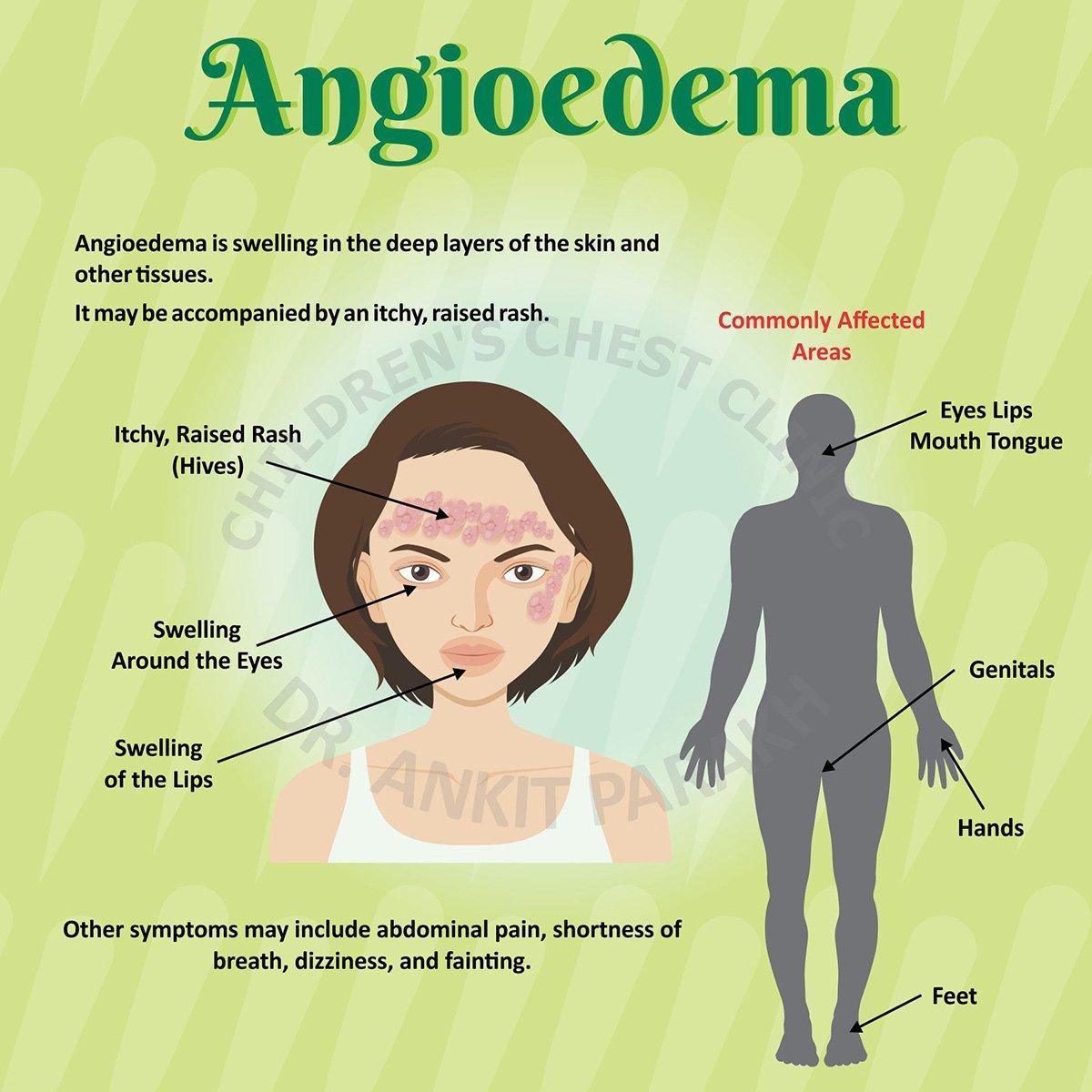
Angioedema is a condition characterized by sudden swelling beneath the skin, often around the eyes, lips, throat, hands, or feet. It can be triggered by allergies, medications, or even stress. For many people, managing angioedema goes beyond medication dietary choices can play an important role in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups. While medical treatment (such as antihistamines or prescribed drugs) is often necessary, adjusting what you eat may help control symptoms and support long-term wellness.
Understanding Angioedema and Its Triggers
Angioedema involves swelling in the deeper layers of the skin, often caused by fluid buildup. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-lasting), with triggers varying from person to person. Common causes include:
-
Food allergies shellfish, nuts, dairy, and eggs are common culprits.
-
Medications including ACE inhibitors and certain antibiotics.
-
Environmental allergenspollen, dust, or insect stings.
-
Idiopathic causesin some cases, the cause remains unknown.
Because food is one of the most frequent triggers, dietary management is a practical and proactive way to control flare-ups.
The Role of Diet in Angioedema
1. Identifying Food Allergens
The first step in using diet to manage angioedema is identifying which foods provoke a reaction. Keeping a food diary can help pinpoint triggers. For example, someone may notice that their swelling episodes occur after consuming shellfish or artificial food additives. Once identified, eliminating these triggers can significantly reduce flare frequency.
2. Avoiding Histamine-Rich Foods
Histamine is a natural compound in the body involved in allergic responses. Foods high in histamine can worsen angioedema for some people. These include:
-
Aged cheeses
-
Processed meats
-
Fermented foods (sauerkraut, soy sauce)
-
Alcohol (especially red wine)
By reducing intake of histamine-rich foods, patients may experience fewer flares.
3. Supporting Gut Health
Research suggests that gut health plays a role in allergic responses. Eating a diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics can help balance gut bacteria and may reduce inflammatory responses. Yogurt, kefir, bananas, and whole grains are good additions.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Foods
A diet emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods may also help manage angioedema symptoms. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts, flaxseeds) and antioxidants (berries, leafy greens, turmeric) can help lower inflammation in the body.
Foods That May Worsen Angioedema
Certain food groups are more likely to exacerbate angioedema flares:
-
Dairy productscommon allergen, especially milk and cheese.
-
Shellfish and fishtop triggers for allergic reactions.
-
Tree nuts and peanutsfrequently linked to swelling episodes.
-
Processed foodsoften contain additives, dyes, or preservatives that act as triggers.
-
Gluten-containing grainsfor those with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease.
Elimination diets, under the supervision of a healthcare provider, can help determine which of these foods should be removed long-term.
Hydration and Lifestyle Considerations
In addition to dietary changes, hydration is key. Drinking enough water helps flush excess histamine and toxins from the system. Limiting alcohol and caffeine, both of which can dehydrate the body and increase inflammation, is also recommended.
Other lifestyle factors include:
-
Stress managementstress can worsen angioedema flares. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing may help.
-
Regular exercisepromotes circulation and reduces overall inflammation.
-
Adequate sleeppoor sleep can weaken the immune system, making flare-ups more likely.
Medical Support and Diet: A Combined Approach
While diet can make a difference, many patients also need medical treatment to manage angioedema. Antihistamines, corticosteroids, or specific drugs like C1 esterase inhibitors are commonly prescribed. In bacterial-related swelling cases or secondary infections, antibiotics may be used.
This is where the healthcare supply chain, including cephalexin capsules distributors, plays a vital role. Cephalexin is a widely used antibiotic that treats bacterial infections, which can sometimes complicate angioedema or mimic similar swelling symptoms. Reliable distributors ensure that pharmacies, hospitals, and clinics have timely access to these medications. For patients, this availability means quicker treatment and reduced risks when infections overlap with chronic conditions.
The mention of cephalexin capsules distributors in this context underscores the importance of accessibility not only in emergency situations but also in long-term condition management. Just as dietary adjustments are proactive, access to trustworthy pharmaceutical distribution is equally preventative in avoiding complications.
Creating a Practical Diet Plan
Here are some practical steps for those living with angioedema who want to incorporate dietary changes:
-
Track and Eliminate: Start with a food journal. Record meals, snacks, and beverages alongside any symptoms. Gradually eliminate suspect foods.
-
Focus on Fresh, Whole Foods: Choose fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains over processed items.
-
Experiment with Low-Histamine Options: Replace aged cheeses with fresh cheese (like mozzarella), swap red wine with herbal teas, and choose fresh meat over processed.
-
Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Staples: Add turmeric to soups, snack on walnuts, or prepare salmon a couple of times per week.
-
Stay Hydrated: Aim for 6–8 glasses of water daily, adjusting based on activity levels.
-
Consult Professionals: Always work with an allergist, immunologist, or dietitian to ensure nutritional adequacy while eliminating triggers.
The Bigger Picture
Managing angioedema requires a comprehensive approach. While medication is critical for acute flare-ups, diet can significantly influence the long-term pattern of symptoms. For many patients, combining professional care, personalized dietary adjustments, and stress management strategies results in fewer episodes and improved quality of life.
Equally important is ensuring that when medical treatment is necessary whether antihistamines or antibiotics patients have access to safe and effective options. That’s why cephalexin capsules distributors and other pharmaceutical suppliers remain essential partners in the broader healthcare system. Their role ensures continuity of care, particularly in urgent cases where infections or complications may arise alongside angioedema.
Conclusion
Dietary changes offer a powerful tool for people with angioedema to manage and potentially reduce flare-ups. By identifying and eliminating triggers, prioritizing anti-inflammatory foods, and supporting overall wellness through hydration and lifestyle, individuals can take proactive control of their condition. At the same time, medical treatment and reliable access to medications facilitated by trusted cephalexin capsules distributors remain crucial components of comprehensive care.
For anyone dealing with angioedema, the best results come from an integrated approach: mindful eating, healthy habits, and collaboration with healthcare providers.